The greenhouse effect is the name given to a natural phenomenon whereby solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere and warms the planet.
Greenhouse gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and ozone allow incoming sunlight to pass through but then prevent some of the heat from escaping back out into space.
This trapped heat makes Earth’s average temperature warm enough to support life.
However, human activities are now causing an unprecedented increase in greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, which amplifies the greenhouse effect and is resulting in global warming. One of these human-caused greenhouse gases is chlorofluorocarbon (CFC), which was once widely used as a refrigerant in air conditioners. CFC molecules are very stable and do not react with other atmospheric constituents.
As a result, they can linger in the atmosphere for years or even decades after being emitted. Once in the stratosphere—the uppermost layer of Earth’s atmosphere—CFC molecules break down under ultraviolet light from the sun, releasing chlorine atoms that catalyze reactions that destroy ozone molecules. The loss of stratospheric ozone depletes Earth’s natural sunscreen, leading to an additional warming of our planet.

How Do Air Conditioners Contribute to Global Warming? An Overview
Are you wondering “How Do Air Conditioners Contribute to Global Warming?” While the primary purpose of an air conditioner is to cool your home, it also has an impact on the environment. specifically, air conditioners contribute to global warming.
Here’s how:
a. Air conditioners emit greenhouse gases
Air conditioners use refrigerant gas that helps to cool the air inside your home. This refrigerant gas is a fluorinated hydrocarbon, which is classified as a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to global warming.
b. Electricity production for air conditioners emits more greenhouse gases
In order to power your air conditioner, electricity must be produced. The majority of electricity in the United States comes from power plants that burn fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. burning these fossil fuels emits more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, further contributing to global warming.
So, while air conditioners may make your home more comfortable during hot weather, they also have an impact on climate change. To help reduce this impact, consider investing in an energy-efficient model and making sure that it’s properly maintained so that it doesn’t leak refrigerant gas into the atmosphere.
How Much Do Air Conditioners Contribute to Global Warming?
Air conditioners are one of the most common household appliances, and they have a significant impact on both energy use and greenhouse gas emissions.
In the United States, air conditioners account for about 6% of all residential electricity consumption – totaling more than $11 billion annually in electric bills and nearly 200 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
While there are many different types and sizes of air conditioners, they all work by moving heat from the inside of a building to the outside.
This process uses a lot of energy, which results in increased greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, air conditioners are responsible for about 1% of global greenhouse gas emissions each year. There are some ways to reduce the impact of air conditioners on climate change.
For example, using more efficient models can help save energy and money while also reducing emissions. Additionally, properly maintaining your air conditioner can also improve its efficiency and prevent it from leaking harmful refrigerants into the atmosphere.
Why Air Conditioning is Bad for the Environment?
It’s no secret that air conditioning can be bad for the environment. In fact, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), air conditioners are one of the top consumers of energy in the United States.

The EPA estimates that air conditioners use about 6% of all the electricity produced in the country, and this number is only expected to rise as more and more people purchase air conditioners.
But why exactly is air conditioning so bad for the environment?
There are a few reasons:
1. Air conditioners use a lot of energy:
As we mentioned before, AC units are some of the biggest energy hogs in our homes. This means that when you run your air conditioner, you’re contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
2. Air conditioners release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere:
Most AC units use Freon or other refrigerants to cool down your home. These chemicals are known to be damaging to the ozone layer, and they can also contribute to smog formation and acid rain.
3. Air conditioners can make your home too comfortable:
When your home is too comfortable, you’re likely to spend more time indoors where there isn’t any natural ventilation or breezes blowing around. It will enhance the uses time of air conditioning and thus increase the emission of CO2 and burn more energy contributing to global warming.
Why is AC Bad for Climate Change?
Air conditioners are one of the biggest contributors to climate change. They use a lot of energy to cool down your home, which in turn releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun and cause the Earth’s temperature to rise.
While air conditioners are essential for many people during hot weather, there are some things you can do to reduce their impact on the environment.
First, make sure your air conditioner is properly insulated and maintained. This will help it run more efficiently and use less energy.
Second, consider using fans or other alternatives to air conditioning when possible.
Finally, look for air conditioners that have earned Energy Star certification – these products meet strict efficiency guidelines set by the US Environmental Protection Agency and can save you money on your energy bills while helping protect the planet.
How Does Air Conditioner Emit Greenhouse Gases?
It is a common misconception that air conditioners do not emit greenhouse gases. In fact, all air conditioners emit greenhouse gases, but the amount emitted depends on the type of air conditioner and how it is used.
The most common type of air conditioner is the split-system air conditioner, which uses refrigerant to cool and circulate air.
When this refrigerant leaks, it can escape into the atmosphere and contribute to climate change. In addition, split-system air conditioners use electricity to power their compressors. The production of this electricity emits greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as well.
If you are concerned about reducing your impact on climate change, there are a few things you can do to minimize the emissions from your air conditioner. First, make sure that your air conditioner is properly maintained so that it doesn’t leak refrigerant. Second, choose an energy-efficient model when buying a new air conditioner.
And finally, use your air conditioner less by taking steps to keep your home cooler without relying on artificial cooling.
How Do Air Conditioners Contribute to Global Warming?
Air conditioners contribute to global warming in two primary ways. First, they consume a lot of energy, often produced from burning fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
These gases trap heat and lead to a rise in the Earth’s average temperature
. Second, air conditioners use and sometimes leak refrigerants, which are potent greenhouse gases themselves. Therefore, the widespread use of air conditioners exacerbates global warming.
Does AC Cause Air Pollution?
You may not think of air pollution and acne as being connected, but there is some evidence that air pollution can cause or worsen acne. Acne is a skin condition that occurs when the hair follicles become clogged with sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria. The exact cause of acne is unknown, but it is thought to be related to hormone changes, genetics, and inflammation.

There are several types of air pollutants that have been linked to acne. These include particulate matter (PM), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). Particulate matter is a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air.
Ozone is a gas that forms when sunlight reacts with certain chemicals in the atmosphere. Nitrogen dioxide is a gas that comes from car exhaust and power plants. Sulfur dioxide is a gas that comes from burning fossil fuels such as coal and oil.
One study found that exposure to PM10 – tiny particulate matter less than 10 micrometers in diameter – was associated with an increased risk of developing acne vulgaris, the most common type of acne. The study also found that people who lived in areas with high levels of NO2 were more likely to have severe acne than those who lived in areas with lower levels of NO2. Another study looked at the effect of O3 on people with acne vulgaris and found that exposure to O3 worsened their symptoms.
So what does this all mean? There is some evidence linking air pollution to the development or worsening of acne, but more research needs to be done to confirm these findings.
How Air Conditioners Affect the Ozone Layer
As the hot summer months approach, many of us begin to think about how we will stay cool during the dog days ahead. For most of us, that means firing up the air conditioner. But did you know that air conditioners can have a negative impact on the ozone layer?
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are chemicals used in air conditioners that help to cool the air. However, CFCs are also known to damage the ozone layer. The ozone layer is a thin shield of gas that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
When CFCs are released into the atmosphere, they break down this protective layer, leaving us vulnerable to UV radiation. There are some things you can do to help reduce the impact of your air conditioner on the ozone layer. Look for an energy-efficient model – these use less power and generate fewer emissions.
Make sure your unit is properly maintained and serviced – leaks can release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere. And when it’s time to replace your old unit, choose one with a low global warming potential (GWP). By taking these simple steps, you can help keep our planet healthy and ensure that future generations can enjoy summers free from harmful UV rays.
How Air Conditioner Affect Global Warming?
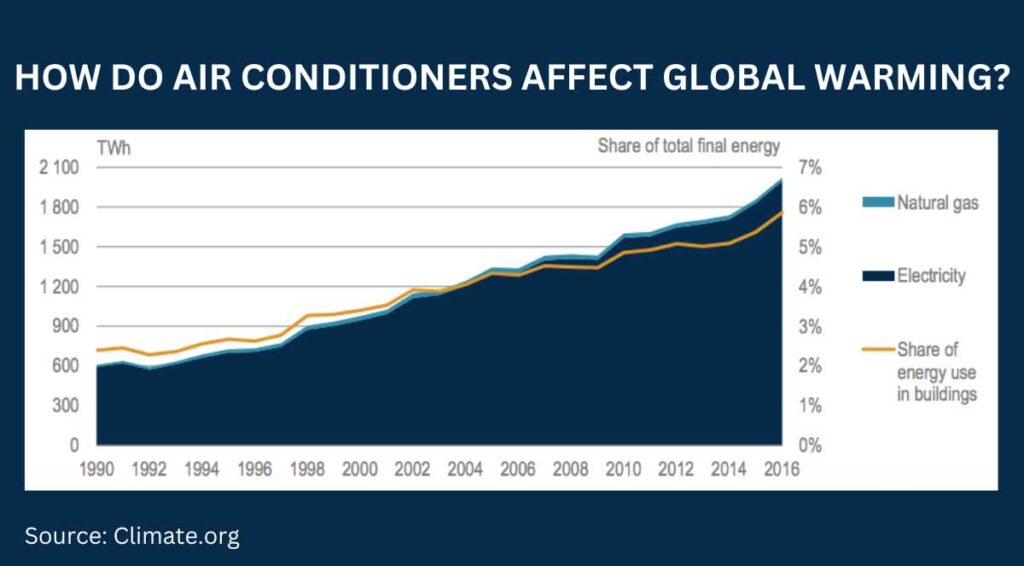
Air conditioners play a significant role in contributing to global warming. Air conditioning units emit a large amount of greenhouse gases, particularly hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which have a high global warming potential.
These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to increased temperatures, changes in weather patterns, and rising sea levels.
Additionally, air conditioners require a significant amount of energy to operate, which is often generated from fossil fuels, further releasing harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
To mitigate the impact of air conditioners on global warming, it is essential to reduce our reliance on them, adopt more energy-efficient alternatives, and support the development of greener technologies.
Reduce Heat And Air Conditioning to Fight Global Warming
Most people think of global warming as something that happens outdoors. But the fact is, our homes and businesses are responsible for a large percentage of greenhouse gas emissions. In the United States, buildings account for 39% of all energy use and 68% of electricity consumption.
And a significant portion of that energy is used to heat and cool our buildings. There are many ways to reduce the amount of energy used for heating and cooling, which can help fight global warming. Some simple measures include:
• Keeping your thermostat at 78 degrees or higher in the summer and 68 degrees or lower in the winter. Every degree above 78 in the summer can add 3-5% to your cooling costs.
• Using ceiling fans to circulate air and make rooms feel cooler without actually changing the temperature.
• Taking advantage of natural ventilation by opening windows on cool days and nights.
How Much Heat Does an Air Conditioner Produce?

We all know that air conditioners are designed to cool us off on hot days, but have you ever wondered how they work? Let’s take a closer look at how much heat an air conditioner produces. Air conditioners use a process called refrigeration to cool the air inside your home.
This process involves removing heat from the air and transferring it to the outside environment. In order to do this, air conditioners use refrigerant, which is a substance that helps transfer heat. The refrigerant passes through a series of coils inside the air conditioner unit.
As it does so, it absorbs heat from the air inside your home and transfers it to the outside environment. This is why you often see condensation on the coils of your air conditioner unit – it’s because the refrigerant is absorbing heat from the air! So, how much heat does an air conditioner produce?
It actually depends on the size of the unit and the temperature difference between the inside and outside of your home. However, most units produce around 3,500 watts of cooling power, which is enough to remove about 12,000 BTUs (British Thermal Units) of heat per hour.
Air Conditioner Greenhouse Gas
An air conditioner is a machine that helps to cool the air in a room or building by circulating refrigerant through it. The refrigerant evaporates and condenses, providing a cooling effect. However, this process also uses energy, which can result in greenhouse gas emissions.
Air conditioners use chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) as their refrigerant. CFCs are powerful greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. When they leak into the atmosphere, they trap heat and cause the Earth’s temperature to rise.
As a result, it’s important to make sure your air conditioner is properly maintained so that it doesn’t leak these harmful gases into the environment. In addition to CFCs, air conditioners also use hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). HFCs are less harmful than CFCs but still contribute to climate change.
Air conditioners that use HFCs can be found in some homes and buildings. If you have an HFC-based air conditioner, make sure it’s well-maintained so it doesn’t leak these gases into the atmosphere.
How Much CO2 Does an Air Conditioner Emit Per Hour
The amount of CO2 an air conditioner emits per hour can vary depending on the model and age of the unit. However, newer units tend to emit less CO2 than older models. For example, a 2009 study found that central air conditioners emitted about 940 pounds of CO2 over their lifetime.
This number will be different for each household, as it depends on how often the unit is used. Nevertheless, it’s important to be mindful of the impact our daily activities have on the environment.
How Much CO2 Does an Air Conditioner Emit?
If you have an air conditioner, you may be wondering how much CO2 it emits. Unfortunately, there is no easy answer to this question. It depends on a number of factors, including the type of air conditioner, the size of the unit, and the efficiency of the unit.
The average air conditioner emits about 1 ton of CO2 per year. However, this number can vary significantly depending on the factors mentioned above. For example, a larger air conditioner will emit more CO2 than a smaller one.
And an older, less efficient air conditioner will emit more CO2 than a newer, more efficient one. If you’re concerned about the amount of CO2 your air conditioner is emitting, there are some things you can do to reduce its emissions. First, make sure your air conditioner is properly sized for your home.
A unit that’s too small or too large will be less efficient and will use more energy (and produce more CO2). Second, regularly maintain your air conditioner to ensure it’s operating at peak efficiency. This includes changing the filters and having them serviced by a qualified technician every few years.
Finally, consider upgrading to a more efficient model when it’s time to replace your old unit. Newer models are much more energy-efficient than older ones and can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
Do Air Conditioners Make Cities Hotter?

Do air conditioners make cities hotter? That’s a complicated question to answer, as it depends on a number of factors. But in general, the answer is yes – air conditioners can make cities hotter.
How does this happen? Well, when an air conditioner cools the air inside a building, that cooled air has to go somewhere. And often, that somewhere is outside.
So the cooled air from the AC unit escapes into the street or alleyway, raising the temperature in those areas. It’s not just one AC unit doing this – it’s all of them in a city working together. As more and more buildings have AC units installed, the problem gets worse and worse.
The heat island effect kicks in, and temperatures start to rise overall in urban areas. So what can be done about it? One solution is to use so-called green roofs – rooftops planted with vegetation that helps keep the building cooler.
Another is to install AC units that don’t vent their cooled air outside but instead recirculate it back into the building. But both of these solutions come with costs and challenges, so finding the right balance isn’t always easy. In short, yes – air conditioners can make cities hotter by contributing to the heat island effect.
But there are ways to mitigate this effect if we’re willing to put in some effort (and money).
Effect of air conditioning gases to global warming:
The effect of air conditioning gases on global warming is significant. Air conditioning systems, particularly those that use hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) as refrigerants, release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
These gases trap heat and contribute to the greenhouse effect, leading to an increase in global temperatures. The widespread use of air conditioning in homes, offices, and vehicles has contributed to the rising levels of these gases.
To mitigate this impact, there is a growing emphasis on transitioning to more environmentally friendly refrigerants and improving the energy efficiency of air conditioning systems. Such measures can help reduce the negative effects of air conditioning gases on global warming.
Conclusion
While air conditioners are amazing at cooling us off, they, unfortunately, contribute to global warming. How? Well, air conditioners use a refrigerant to cool the air inside your home.
This refrigerant is called chlorofluorocarbon, or CFC for short. When this gas is released into the atmosphere, it contributes to the depletion of the ozone layer. Additionally, CFCs are greenhouse gases, which means that they trap heat in the atmosphere and cause global warming.